
Discover the differences between ADHD and learning disabilities, why ADHD is often mistaken for a learning disorder, and how Dr. Adelina Matevosyan at NeuroCognitive Solutions provides expert neuropsychological assessments.
NeuroCognitive Solutions offers a comprehensive resource for understanding the various neuropsych categories that play a crucial role in cognitive evaluations. Our platform is dedicated to providing insights into how neuropsychological assessments can enhance cognitive clarity and overall mental health.
At NeuroCognitive Solutions, we categorize our resources to help users navigate the complex world of neuropsychology. Each category is designed to address specific aspects of cognitive functioning and assessment, making it easier for individuals, families, and professionals to find relevant information tailored to their needs.
Our website features an intuitive layout where you can explore different neuropsych categories, each containing articles, guides, and tools designed to enhance your understanding of neuropsychological evaluations. Whether you are a parent seeking insights for your child or a professional looking for advanced resources, our categories serve as a valuable starting point.By leveraging the information available in these categories, you can empower yourself with knowledge that fosters cognitive clarity and supports mental well-being. Explore NeuroCognitive Solutions today to unlock the potential of neuropsychological evaluations in your life.

Discover the differences between ADHD and learning disabilities, why ADHD is often mistaken for a learning disorder, and how Dr. Adelina Matevosyan at NeuroCognitive Solutions provides expert neuropsychological assessments.

Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are two prevalent neurodevelopmental disorders that can significantly affect a child’s development. Both conditions can occur alongside anxiety, complicating their management. Understanding these disorders through comprehensive neuropsychological assessment is crucial for effective intervention. In this article, we will delve into the importance of these assessments, the role of Dr. Adelina Matevosyan at Neurocognitive Solutions, and the specific testing methods used for ADHD and Autism.
ADHD is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD may struggle with focusing, following instructions, and managing their impulses, leading to challenges in academic and social settings. Conversely, Autism is marked by difficulties in social interaction, communication challenges, and restricted or repetitive behaviors. While ADHD and Autism are distinct conditions, they often co-occur, complicating diagnosis and treatment.

Children with ADHD may exhibit various symptoms, which can be categorized into two main types:
Autism presents a different set of challenges, which may include:
Understanding these symptoms is essential for parents and educators to provide appropriate support and interventions.
Research indicates a strong relationship between ADHD, Autism, and anxiety disorders. Many children with ADHD also experience anxiety, which can exacerbate attention difficulties and emotional dysregulation. Anxiety can manifest as excessive worry about performance, social interactions, or changes in routine.
For children with Autism, anxiety may arise from difficulties in social situations and a struggle to navigate the complexities of interactions. Children may feel overwhelmed in unfamiliar environments or when faced with unexpected changes. This interconnectedness emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach to assessment and treatment.
Neuropsychological assessments are comprehensive evaluations conducted by a clinical neuropsychologist. These assessments aim to evaluate a child’s cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functioning. For children suspected of having ADHD or Autism, these assessments provide valuable insights into their strengths and weaknesses, helping clinicians and parents understand the best way to support their development.
This multifaceted approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of a child’s unique challenges and capabilities.
Dr. Adelina Matevosyan is a highly skilled neuropsychologist specializing in the assessment and treatment of ADHD and Autism. Her approach combines clinical expertise with a deep understanding of neurocognitive processes. Dr. Matevosyan employs a variety of assessment tools to create a tailored profile for each child, ensuring that interventions are personalized to their unique needs.

Dr. Matevosyan has extensive experience in working with children and families, emphasizing a compassionate and supportive approach. Her expertise includes:
ADHD neuropsychological testing focuses on evaluating attention, executive functioning, memory, and processing speed. Commonly used tests include:
These tests help identify specific areas where a child may struggle, allowing for targeted interventions.
Neurocognitive Solutions is dedicated to providing individualized assessments and treatment strategies for children with ADHD and Autism. Their holistic approach focuses on not only identifying challenges but also developing effective coping strategies and interventions.
For families navigating ADHD and Autism, understanding and coping strategies are essential. Here are some strategies parents can implement:
1. What is the difference between ADHD and Autism?
ADHD primarily affects attention and impulse control, while Autism encompasses a broader range of social and communication challenges. While both conditions can co-occur, understanding their distinct features is essential for effective treatment.
2. How are ADHD and Autism diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical interviews, behavior assessments, and neuropsychological testing. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified neuropsychologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
3. Can ADHD and Autism be treated?
Yes, treatment often involves a combination of behavioral therapy, medication, and educational support. Tailored interventions based on individual assessment results are most effective.
4. What role does anxiety play in ADHD and Autism?
Anxiety can significantly impact children with ADHD and Autism, exacerbating symptoms and making it harder for them to function. Addressing anxiety through therapy and coping strategies is vital for overall well-being.
Understanding ADHD and Autism through neuropsychological assessment is vital for providing effective support to children and their families. Dr. Adelina Matevosyan and her team at NeuroCognitive Solutions offer expertise and individualized approaches to address these complex disorders. By utilizing comprehensive testing methods and developing tailored interventions, families can navigate the challenges of ADHD and Autism more effectively.
For more information on assessments, consultation, and resources, visit the following links:

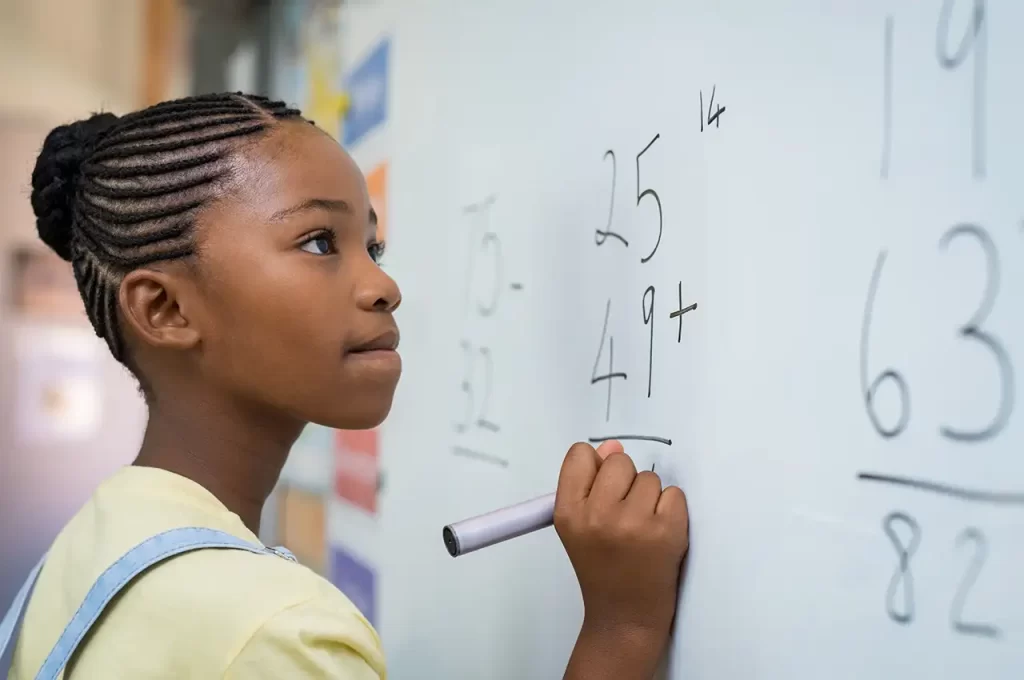
In our increasingly complex and technology-driven society, mastering mathematical concepts has become a fundamental skill for success. Mathematics is not just a subject taught in school; it is a universal language of logic and reasoning that permeates various professions and everyday life. Yet, a significant number of students find themselves grappling with mathematical concepts, often due to deficiencies in visual spatial skills. Understanding these skills and their critical role in cognitive processes is essential for enhancing mathematical proficiency. This article will explore visual spatial skills in depth, their significance in mathematics, and how neuropsychological testing can identify areas for improvement.
Visual spatial skills refer to the ability to perceive, analyze, and interpret visual information in a spatial context. These skills enable individuals to manipulate objects mentally, understand how they fit together, and navigate through physical space. They are essential for a variety of activities, from solving complex geometry problems to interpreting graphs and diagrams.

A child engaged in activities designed to enhance visual spatial skills, emphasizing the role of neuropsych testing in pediatric neuropsychology.
Visual spatial skills can be broken down into several key components:
Spatial Visualization: This is the ability to visualize and manipulate objects in a three-dimensional space. Spatial visualization is critical for understanding concepts such as volume and surface area in geometry.
Spatial Orientation: This refers to understanding the position of objects in relation to oneself and other objects. It allows individuals to navigate their environment effectively.
Spatial Perception: The ability to accurately perceive spatial relationships between objects is fundamental for tasks such as reading maps or interpreting blueprints.
Mental Rotation: This is the capacity to rotate objects mentally to understand their configurations. This skill is particularly important in geometry and physics, where visualizing the movement or rotation of objects is essential.
These components work together to facilitate mathematical understanding. For example, a student who can visualize the rotation of a geometric shape will likely find it easier to grasp concepts in geometry and trigonometry.
Beyond academia, visual spatial skills are crucial in various fields. Engineers, architects, and designers rely heavily on these skills to create and interpret blueprints and models. In the medical field, professionals must understand complex anatomical structures in three dimensions. Everyday tasks, such as driving or assembling furniture, also demand strong visual spatial abilities, showcasing their importance in daily life.
In professions such as art and design, visual spatial skills play a vital role in creating aesthetically pleasing and functional works. Graphic designers, for instance, need to visualize how different elements of a design will interact within a space. In sports, athletes often use visual spatial skills to anticipate the movements of other players and respond accordingly. This highlights the widespread applicability of these skills beyond traditional academic settings.
Research consistently demonstrates a strong correlation between visual spatial skills and mathematical ability. Students who struggle with math often exhibit deficiencies in their visual spatial skills. For example, a child who has difficulty visualizing geometric shapes may find geometry challenging. Similarly, a student who cannot interpret graphs may struggle with algebraic concepts that rely on visual data representation.
Numerous studies have examined the relationship between visual spatial skills and mathematical performance. One influential study conducted by Mix et al. (2002) found that spatial skills were significant predictors of mathematical performance in children. The researchers noted that children with strong spatial skills outperformed their peers in various math tasks, including geometry and problem-solving.
Another study by Newcombe (2006) emphasized the importance of spatial skills in early math development. The findings suggested that spatial skills could be developed through targeted interventions and that fostering these skills in young children could lead to improved math performance later on.
To further illustrate the connection between visual spatial skills and math, consider the case of two students: Alex and Jamie. Both students are in the same math class, but their performance levels differ significantly.
Alex excels in math and often scores high on tests. He has strong visual spatial skills, which allow him to quickly visualize and manipulate geometric shapes in his mind. He easily understands concepts like area, volume, and angles because he can mentally rotate and arrange shapes.
In contrast, Jamie struggles with math, particularly in geometry. She has difficulty visualizing shapes and understanding how they relate to one another. This limitation affects her ability to solve problems and grasp key mathematical concepts. Through neuropsychological testing, it is discovered that Jamie has significant deficits in her visual spatial skills. With targeted interventions focused on enhancing these skills, Jamie begins to improve in her math performance.
To accurately assess a student’s visual spatial skills, neuropsychological testing is essential. This form of cognitive testing evaluates various cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and visual spatial processing. A comprehensive cognitive assessment system can identify specific areas where a student may need support, guiding targeted interventions to enhance their learning experience.
Neuropsychological testing involves a series of standardized tasks designed to measure cognitive abilities. These assessments can reveal strengths and weaknesses in visual spatial skills, helping educators tailor their teaching strategies accordingly.
For instance, if a student demonstrates difficulty in spatial visualization, targeted interventions can be developed to enhance that skill through specific exercises and activities. Dr. Matevosyan specializes in neuropsych testing, providing tailored assessments that focus on visual spatial skills. By using these assessments, educators and parents can gain a deeper understanding of a child’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses. For more information on Dr. Matevosyan’s services, visit our consultation page.
Neuropsychological tests can vary widely, but some common assessments used to evaluate visual spatial skills include:
Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test: This test requires individuals to copy a complex figure and then reproduce it from memory. It assesses visual organization and memory.
Block Design Test: Participants use blocks to create specific designs, measuring spatial visualization and construction abilities.
Visual-Spatial Processing Tests: Various tests assess how well individuals can perceive and manipulate visual information, such as identifying shapes or understanding spatial relationships.
Educators play a critical role in the testing process. By observing students in the classroom and identifying potential areas of concern, teachers can recommend students for testing. Early identification of visual spatial deficits allows for timely interventions, ultimately supporting students’ academic growth.
Improving visual spatial skills can lead to better performance in math and other related subjects. Here are some strategies that can help:
Engaging in activities that require spatial reasoning can significantly strengthen visual spatial skills. Puzzles, 3D modeling, and spatial video games encourage players to think critically about spatial relationships. Board games that involve strategy, such as chess or tangrams, can also enhance spatial awareness.
Puzzles, in particular, are excellent tools for developing visual spatial skills. Jigsaw puzzles require individuals to visualize how pieces fit together, promoting problem-solving and critical thinking. Similarly, three-dimensional puzzles, like those made of blocks or geometric shapes, help reinforce spatial visualization skills.
Using physical objects to explore mathematical concepts can aid in developing visual spatial understanding. For example, manipulatives in math lessons, such as blocks or geometric shapes, allow students to visualize relationships between numbers and concepts. This tactile approach helps bridge the gap between abstract ideas and concrete understanding.
Building Projects: Engaging students in building projects, such as constructing models of geometric shapes, helps reinforce their understanding of spatial relationships.
Interactive Math Games: Games that require students to physically move pieces to solve problems can enhance spatial reasoning. For example, using dice to explore probability and counting.
Encouraging students to draw out problems or visualize solutions can reinforce their ability to manipulate and understand spatial relationships. Activities like sketching geometric figures or creating diagrams can solidify comprehension and promote active engagement in learning.
Visualization is a powerful tool in mathematics. When students are taught to visualize problems, they can often see solutions more clearly. For instance, drawing a diagram of a word problem can help students understand the relationships between different elements and identify the steps needed to solve it.
In the digital age, numerous apps and software are designed to enhance visual spatial skills through interactive learning experiences. Programs that focus on geometry, spatial reasoning, and problem-solving can be particularly effective in promoting these skills. Educational technology provides students with immediate feedback and opportunities for practice in a fun, engaging manner.
Geometry Dash: A platformer game that involves navigating through obstacles, enhancing spatial reasoning skills through gameplay.
Tinkercad: An online 3D modeling tool that allows students to design and visualize objects, promoting spatial awareness and creativity.
Lumosity: A brain-training app that offers games designed to enhance cognitive skills, including visual spatial abilities.
If you’re interested in personalized strategies to boost visual spatial skills, Dr. Matevosyan can provide expert guidance. Learn more about the services offered here.
Implementing a cognitive assessment system can provide valuable insights into a student’s learning profile. These assessments not only identify strengths and weaknesses in visual spatial skills but also help in crafting tailored educational plans. Regular assessments ensure that progress is monitored and adjustments are made as needed.
Regular assessments play a crucial role in the educational process. They allow educators to track student progress, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and make informed decisions regarding future instructional strategies. By incorporating assessments into the learning process, educators can provide timely support to students in need.
Understanding a student’s learning profile can help educators tailor their instruction to fit individual needs, making learning more effective. By identifying whether a student thrives with visual aids, hands-on activities, or auditory instructions, teachers can adapt their teaching strategies accordingly. This personalized approach not only enhances engagement but also improves retention of mathematical concepts.
When neuropsychological assessments indicate specific areas of concern regarding visual spatial skills, collaboration with specialists becomes vital. Educators can work alongside psychologists, special education professionals, and tutors to develop a comprehensive support plan. This collaborative effort ensures that interventions are multifaceted and tailored to address the unique needs of each student.
After assessments are conducted, providing feedback to students and parents is crucial. This feedback can demystify the assessment results, making them understandable and actionable. Educators should explain the implications of the findings, discuss strengths, and outline areas for growth. Open dialogue about assessment results fosters a growth mindset, encouraging students to view challenges as opportunities for improvement.
Educators and parents play a crucial role in supporting the development of visual spatial skills. By fostering a positive learning environment and utilizing effective strategies, they can help students enhance these essential skills.
Open communication between teachers and parents is vital for a child’s success. Regular updates on a child’s progress can lead to more targeted support at home and in school. For instance, if a teacher notices a student struggling with spatial tasks, they can share specific strategies that parents can use at home to reinforce these skills.
Creating a supportive learning environment at home encourages exploration and curiosity. Parents can integrate learning activities into daily life, such as cooking (measuring ingredients), gardening (understanding space and shapes), or home improvement projects (following plans). These activities not only foster visual spatial skills but also strengthen the parent-child bond.
Encourage Exploration: Allow children to explore their environment, providing opportunities for them to navigate and understand spatial relationships. Taking walks and asking them to describe the layout of their surroundings can be beneficial.
Engage in Conversation: Discuss shapes, sizes, and spatial relationships during everyday activities. This reinforces the relevance of visual spatial skills in daily life. For example, when shopping, ask them to estimate distances between items.
Model Problem-Solving: Show children how to approach spatial problems by modeling the thought process. When assembling a piece of furniture, explain the spatial relationships involved and encourage them to participate.
Create a Stimulating Environment: Fill the home with spatially challenging activities, such as puzzles, building sets, and art supplies that encourage 3D thinking and creativity.
Limit Screen Time: While some digital tools can be beneficial, encourage children to engage in physical activities that require them to use their visual spatial skills in real-world contexts.
Educational institutions can play a pivotal role in developing visual spatial skills by integrating them into the curriculum. This can be achieved through a variety of methods.
Project-based learning encourages students to engage in hands-on, real-world projects that require them to apply their visual spatial skills. For example, a project to design a small park could involve planning the layout, considering distances, and visualizing how different elements will fit together in space. Such projects enhance not only visual spatial skills but also teamwork and problem-solving abilities.
Mathematics classes should emphasize the importance of visual spatial skills through targeted activities. This can include using geometric modeling software, engaging in interactive geometry lessons, or employing manipulatives that help students visualize complex concepts. Incorporating spatial reasoning tasks into assessments can also provide insight into students’ understanding.
Art and design classes can serve as excellent avenues for developing visual spatial skills. Students can explore concepts of symmetry, proportion, and perspective through drawing, painting, and sculpting. These activities encourage creative thinking while reinforcing spatial understanding.
Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) programs can integrate visual spatial skill development by encouraging students to engage in activities such as robotics, coding, and engineering challenges. These fields inherently rely on spatial reasoning, making them ideal for honing these skills.
Educators themselves must be equipped with the knowledge and resources to effectively teach visual spatial skills. Professional development opportunities focusing on spatial reasoning and its importance in education can empower teachers to implement effective strategies in their classrooms.
It’s essential to consider that visual spatial skills can be influenced by cultural factors. Different cultures may place varying degrees of emphasis on spatial skills, which can affect educational outcomes.
For instance, in some cultures, spatial reasoning may be developed more through outdoor play and exploration, while others may focus on structured learning environments. Recognizing these differences is crucial for educators working in diverse classrooms. Tailoring approaches to align with students’ cultural backgrounds can enhance engagement and effectiveness.
Engaging the community in supporting visual spatial skill development can also have a significant impact. Schools can partner with local organizations, museums, and businesses to create programs that promote spatial skills through real-world applications. Field trips to science centers or engineering firms can provide students with hands-on experiences that reinforce classroom learning.
As we look ahead, the importance of visual spatial skills in education and beyond will only continue to grow. The rapid advancement of technology and the increasing complexity of many professions mean that these skills will be essential for future generations.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are becoming powerful tools for enhancing visual spatial skills. These technologies can create dynamic, interactive environments where students can visualize complex concepts, manipulate virtual objects, and practice spatial reasoning in ways that traditional methods cannot offer. For instance, using VR to explore geometric shapes can help students better understand their properties and relationships.
Future research should focus on developing and validating targeted interventions for improving visual spatial skills in diverse populations. Understanding how these skills can be nurtured in different learning contexts will be essential in designing effective educational programs. Researchers should also explore the long-term effects of enhanced visual spatial skills on academic and professional success.
Education policymakers should prioritize visual spatial skill development within curricula and assessment frameworks. By recognizing the role of these skills in overall academic achievement, policies can be implemented to ensure that all students have access to the resources and support they need to develop them.
Ultimately, developing visual spatial skills is not just about improving math performance; it’s about equipping students with the cognitive tools they need to navigate an increasingly complex world. By investing in these skills, we prepare students for success not only in mathematics but in their future careers and everyday life. As educators, parents, and society, we must commit to fostering environments that prioritize the development of these essential skills.
In summary, enhancing visual spatial skills is a multifaceted endeavor that involves parents, educators, and the community. By understanding the significance of these skills and implementing targeted strategies, we can support students in overcoming challenges and achieving their full potential in mathematics and beyond. As we move forward, it is crucial to embrace innovative approaches and collaborate across disciplines to ensure that visual spatial skill development remains a key focus in education.
For anyone interested in personalized strategies to boost visual spatial skills, Dr. Matevosyan can provide expert guidance tailored to individual needs. To get started on your journey toward enhancing visual spatial skills, feel free to contact us today. For more insights into cognitive development and related topics, visit our blog.
By focusing on visual spatial skills and their connection to math success, we can provide targeted support that leads to improved academic performance. Remember, the journey to understanding and enhancing cognitive skills is a collaborative effort involving students, parents, and educators, paving the way for a brighter future for all learners.
FURTHER INFORMATION CAN BE FOUND IN INSTITUTION PUBLISHED JOURNALS:

Navigating childhood can be a complex journey filled with ups and downs. For some children, these challenges may involve cognitive or emotional hurdles that require specialized support. A neuropsychologist can help children understand and overcome these hurdles, providing vital support and strategies for success. Early intervention is crucial; research shows that the sooner children receive assistance, the better their outcomes tend to be. By identifying and addressing issues early, families can help their children thrive academically and socially.
Neuropsychology is a specialized field that focuses on the intricate relationship between the brain and behavior. It encompasses various cognitive functions such as memory, attention, language, and executive functioning, which are essential for everyday tasks. Distinguishing neuropsychology from general psychology is important; while psychologists may focus on behavior and emotional health, neuropsychologists delve into the biological basis of these behaviors.
Cognitive neuropsychology specifically examines how cognitive processes influence a child’s ability to learn and interact with their environment. This field is particularly relevant for children who face challenges in school or social settings, as it provides a framework for understanding the cognitive deficits that may be at play.

A pediatric neuropsychologist conducts a personalized assessment with a child, showcasing the supportive environment at NeuroCognitive Solutions.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry found that children with learning disabilities often have underlying neuropsychological issues, such as deficits in working memory and processing speed (Gathercole & Alloway, 2008). Understanding these deficits can lead to more effective interventions tailored to each child’s unique needs.
The Role of Pediatric Neuropsychologists
A pediatric neuropsychologist specializes in assessing and treating children facing learning and behavioral challenges. Dr. Adelina Matevosyan, with extensive experience in this field, plays a crucial role at NeuroCognitive Solutions. She employs evidence-based methods to identify cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
One of the primary responsibilities of a pediatric neuropsychologist is conducting comprehensive assessments. This process involves a series of standardized tests and observational techniques designed to evaluate various cognitive domains, including attention, memory, language, and executive functioning.
For example, Dr. Adelina Matevosyan employs a combination of formal assessments and informal observations to gather a holistic view of a child’s cognitive abilities. She may administer tasks that assess working memory, problem-solving skills, and processing speed. These evaluations often include parent and teacher questionnaires to provide additional context about the child’s behavior and academic performance in different settings.
Through these assessments, Dr. Matevosyan identifies cognitive strengths and weaknesses that can inform individualized treatment plans. For instance, if a child struggles with executive functioning—such as organizing tasks or managing time—interventions can be tailored to address these specific challenges.
Once assessments are complete, pediatric neuropsychologists like Dr. Matevosyan develop personalized intervention strategies based on the results. This may involve recommending specific educational accommodations, such as extended time for tests or the use of assistive technology.
Moreover, interventions often extend beyond the classroom. Dr. Matevosyan collaborates with parents, teachers, and other professionals to create a comprehensive support system. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone involved in the child’s life is equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to support their development effectively.
For instance, if a child is diagnosed with dyslexia, Dr. Matevosyan may recommend targeted reading interventions that focus on improving phonological awareness and decoding skills. This is how a neuropsychologist can help children and this could include working with specialized tutors who employ multisensory learning techniques, which have been shown to be highly effective for children with learning disabilities.
In addition to cognitive assessments, pediatric neuropsychologists also play a vital role in addressing behavioral challenges. Many children face issues such as anxiety, ADHD, and social difficulties that can impact their academic and social success.
Dr. Matevosyan uses evidence-based approaches to assess these behavioral challenges, incorporating behavioral checklists and direct observations to gain a better understanding of the child’s emotional and social functioning. By identifying underlying cognitive processes contributing to these behaviors, she can recommend appropriate therapeutic strategies.
For example, if a child exhibits anxiety that interferes with their learning, Dr. Matevosyan may recommend cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques to help the child develop coping mechanisms and reduce their anxiety levels. This could include teaching the child relaxation strategies or cognitive restructuring techniques to challenge negative thought patterns.
Another critical aspect of a pediatric neuropsychologist’s role is advocacy. They often serve as liaisons between families, schools, and healthcare providers to ensure that children receive the necessary support and accommodations. Dr. Matevosyan frequently advocates for her clients during Individualized Education Program (IEP) meetings, helping parents navigate the educational system to secure the appropriate resources for their children.
This advocacy extends to educating parents and caregivers about their child’s condition and how to best support them at home. By providing strategies for reinforcing learning and managing behaviors, pediatric neuropsychologists empower families to be active participants in their child’s development.
Research highlights the importance of these evaluations. A study in the Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology indicates that early neuropsychological assessment can lead to better academic outcomes for children with learning difficulties (Sweeney et al., 2018). The findings emphasize that targeted interventions based on neuropsychological assessments can significantly enhance children’s learning experiences.
FIND MORE INFORMATION AT SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS BELOW:

Anxiety and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are two mental health conditions that are commonly diagnosed in children. While they are two separate conditions, there is a high prevalence of anxiety in children with ADHD. In fact, anxiety is often considered a secondary symptom of ADHD, and it can have a significant impact on a child’s academic, social, and emotional development. In this blog, we will explore the relationship between ADHD and anxiety in children, and provide tips and strategies for parents to help their children cope with these conditions.
Both ADHD and anxiety are neurological disorders that affect brain functioning. ADHD is characterized by symptoms such as impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention, while anxiety is characterized by excessive worry, fear, or panic. Recent studies suggest that ADHD and anxiety are linked because they share similar brain circuitry and neurotransmitters. For instance, both ADHD and anxiety involve the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is responsible for motivation and attention. As a result, children with ADHD who have dopamine dysregulation are more susceptible to developing anxiety symptoms.
Anxiety can have several negative impacts on children with ADHD. For example, anxiety can worsen ADHD symptoms such as distractibility, forgetfulness, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD may also experience higher levels of emotional reactivity, which can lead to mood swings and behavioral problems. Furthermore, anxiety can cause a child to withdraw socially, avoid challenges, and become less confident in their abilities. These negative effects can lead to academic struggles, social isolation, and low self-esteem.
The good news is that there are several strategies that parents can use to help their children cope with both ADHD and anxiety. Firstly, parents should work closely with a mental health professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan for their child. This may include medication, behavioral therapy, or a combination of both. Additionally, parents can teach their child coping skills such as positive self-talk, deep breathing, and mindfulness. Engaging in physical activity, getting proper sleep and nutrition, and reducing screen time can also be beneficial. Creating a routine and structure at home can help alleviate anxiety and improve focus as well.
It’s important for parents to provide support and understanding to their child with ADHD and anxiety. Parents can listen to their child’s concerns, validate their feelings, and help them problem-solve their challenges. Being patient, encouraging, and empathetic can foster a positive outlook and reduce stress. Parents can also work with their child’s teachers, school counselors, and healthcare providers to create an individualized education plan (IEP) that addresses their child’s unique needs. This can include accommodations such as extended time for exams, a quiet study environment, and breaks to destress.

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurological condition that affects an individual’s communication, social interaction, and behavior. There is a broad range of symptoms and severity levels, and each individual with ASD is unique in their needs and abilities. High Functioning Autism (HFA) is a term used to describe individuals on the autism spectrum who have average or above-average cognitive and language abilities. However, they may still struggle with social skills, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities.
Individuals with HFA often have difficulty with social interactions, such as interpreting nonverbal cues, initiating and maintaining conversations, and understanding reciprocity. They may also have repetitive behaviors, intense interests, and sensory sensitivities. However, unlike those with other forms of Autism, they may have average or above-average intellectual and language abilities. This can make it challenging for them to fit in with neurotypical peers and lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety.
Getting an accurate diagnosis of HFA is essential for individuals and their families to access the appropriate supports and services. Every person with HFA has unique strengths and challenges, and their support needs will vary depending on their age, environment, and abilities. However, some general strategies that can benefit many individuals with HFA include: